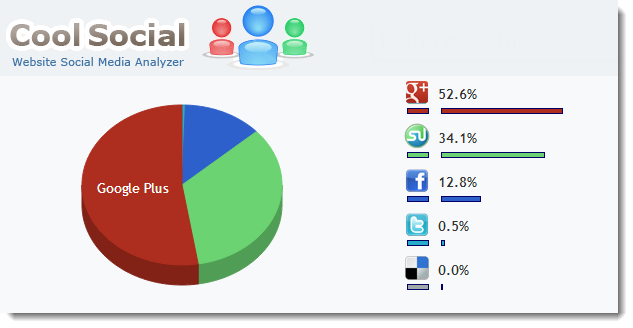
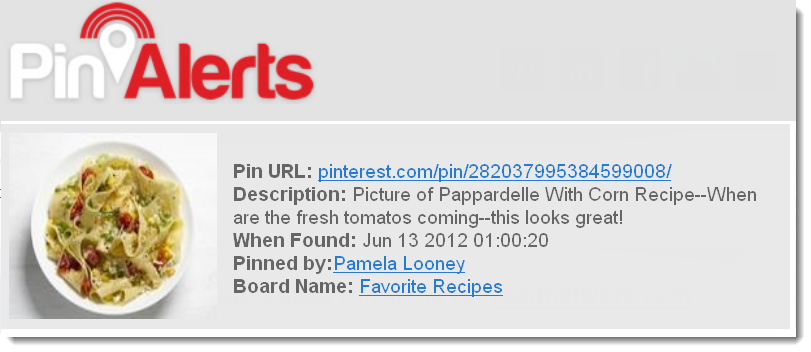
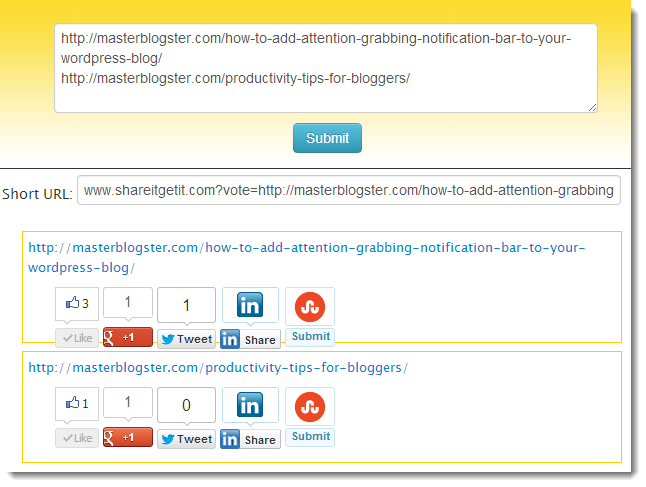
How to make Google fall in love with your article.
Why do you need a blog post that is super SEO friendly? Well, because we all wish that every time we write a new blog post, it quickly ranks well for the main keywords, and we immediately get lots of traffic. Yes, we can share our post to social networks to get a boost in traffic, but that’s a only short term solution. Having a search optimized blog post that ranks well will help you reach audiences for a much longer period of time.
This step by step guide aims to teach you how to make your blog articles SEO friendly. It’s especially helpful for webmasters who are beginners and want to DIY Search Engine Optimization for their site.
I will be focusing on the WordPress blogging platform (since it’s the most popular), and I will be using “How to cook fried rice” as an example of an article I’m trying to optimize.
Step 1: Write a post that you are proud to share with the internet. Aim for excellence.
The single most important rule is to write a really good piece of content. This is by no means easy, but it can potentially render the next few steps redundant. If you write every piece of article knowing your competitors and potential customers are judgingyou based on the content, you’ll naturally put in more effort in coming up with better content. Because it’s highly unlikely that regular webmasters like us can easily churn out the best damn articles ever, it’s much smarter to just aim to create something that’s better than the existing ones.
Here is a dirty trick. Before you start writing, Google the topic you are about to write to look at existing resources.

What can you do to make your post better than theirs?
- Are they lacking in details? Add more details.
- Are they lacking in pictures? Add more images.
- Do they have outdated information? Add updated information.
- Do you have more to add? Make your article longer. (In fact,a study showed that the average content length for a web page that ranks in the top 10 results for any keyword on Google has at least 2,000 words.)
Using a SWOT (Strength, Weakness, Opportunity, Threat) analysis, you can come up with a pretty good plan to craft a better blog post. Now that you’ve got a good idea of how to write good content, here comes the technical part.
Step 2: Keyword in the title + makes it catchy!
The best titles 1) let readers know what they are reading, 2) let search spiders understand the general topic, and 3) entice people to click through to read. There is high SEO value in adding the targeted keywords in the title. It is one of the main on-page ranking factors for search engines like Google.

A title consisting of only targeted keywords would be boring. Add your own twist to it so potential readers can’t help but click on your link. Here’s a pretty easy guide to follow.
Step 3: Know the guidelines for keyword placements
SEO consultants have come a long way from the dark ages of recommending webmasters to stuff keywords all over the place. Your blog post has to be SEO friendly AND human friendly as well. Keywords still play a big part in search engine ranking factors though. Here are some guidelines of where to place your main keywords. Remember: these are not rules set in stone. Overall flow of the content should be natural.
Keyword in URL
Separate your keywords with hyphens, and try to keep your URL as short as possible.

Keyword in headings
Headings are the <h1>, <h2> HTML tags that help to break a content into sections. Think of them as subheadings that help guide the reader along main points of an article. Use keywords in headings when it makes sense to.

Keywords near the start of the article
Here’s the thing about search engines. When they send their spider minions to crawl a web page, they scan from top to bottom. Putting main keywords near the start of the article helps these guys understand the topic quicker, and reminds them that “the article is about this“. Sorry for the simplistic analogy, and as always, use this method when it feels natural.
Variations of keywords repeated 2-3 times throughout the article
Don’t do this.
Humans aren’t stupid. Search engines aren’t stupid either. While it’s important to help search engines understand important content on your page, overdoing it can result in a penalty. Use variations of the keywords. Try using different synonyms. Be natural.
Step 4: Add images, videos, gifs
Nowadays, having a plain old text article is just boring. With social sharing driving increased traffic, you want to make your content as share-worthy as possible. Adding images and videos really do help break up the monotony. Better yet – use gifs! Furthermore, people searching for images might stumble upon your article because of the embedded image.
“Oh, so I just add images and that’s it?”
Credit: www.reactiongifs.com
What you have to do is to make sure relevant keywords are present in the image <alt> tag.

Click on the image in your editor, and you might find additional options (for WordPress).

Under Alternative Text, that is where you have to fill in the appropriate keywords.
Step 5: Link to your older, relevant posts
Also known as internal linking, linking to your own posts should be a priority. I actually covered similar points in one of my older articles about easy ways to increase traffic.
See what I just did
 ?
?
Internal linking helps to pass “link juice” from one page to another; that is, when another site links to your article, the pages that you linked to will also get some of the SEO benefits! You can also direct some traffic to past articles which are collecting virtual dust somewhere on your site.
In WordPress, you only need to highlight a phrase that you want to use as the anchor text, and click the “Insert/edit link” in the toolbar. Either manually insert the URL of your older post, or use the search function to find a relevant page.


Step 6 : Link FROM your older posts
While on the topic of internal linking, why stop at only linking TO your older posts? The benefits go both ways, and in fact, you can help your newer article gain some “link juice” from your older articles by linking FROM them. Not only will people discover your new article when they read your older posts, your newer article might get a boost in search visibility if the articles you are linking from have high link authority.
Here’s a little hack: you can use the same search function mentioned previously to find old posts that contain keywords related to your current article. Type in variations of your targeted keyword and select articles that you think you can link from.
Step 7: Link to credible, authoritative sources
While there is no hard proof that linking out (external linking) to other websites directly affect your own ranking, I am a firm believer in its intrinsic value. Think of it as building good internet karma.
I’d explain why, but I think this article does a better job of explaining why linking out can be good for your own SEO. Also useful to know is WHEN you should link out.
Basically, you are providing a good experience for your readers while laying the foundations for beneficial relationships with other credible sites. When you reference another site, link to them. When you use someone else’s image, link to them.
Step 8: Assign categories and tags
Categories.
When you assign categories, you group content into similar themes. This provides a good way for readers to find articles under a topic they are interested in, and helps search engines understand which contents are closely related to one another.

For Categories, limit each blog post to a maximum of 2 categories. In the case for our article, it would be best to file it under “Rice recipes”. Limiting your categories also ensures a focused theme.
Tags.
While Categories are broader concepts, Tags are more specific to each post. Think of Tags as your website’s index: short keywords that point to you the articles that used them.

For our fried rice recipe, using “rice” as a tag is one option. I might consider “eggs”, or “fried” as good tags too. While Tags aren’t as limited as Categories, you should take heed not be abuse them. 3-4 tags per post is plenty already.
Step 9: Make your meta description pop!
This final step before you publish your post might not be a direct ranking factor, but it affects whether people are likely to click on your link on search results page. Meta descriptions are typically displayed on search engines as the snippet of text below the clickable links.
Consider the following example (click to enlarge).

To bring the attention to the meta description, I blurred out the Titles. You can see how the more useful meta descriptions are the ones that provide a clearer idea of the content I can expect to read, and I don’t think it’s a coincidence that the ones with better descriptions rank higher.
One thing I have to point out is that you don’t have to always have to fill in the meta description. Google will automatically pick out pick out a section of your content to display to searchers, based on what it thinks is most relevant to what the person is searching for. The drawback is, Google only points out certain keywords, and it definitely lacks the ability we have to make the description interesting.
Take note of these few points when writing your meta description:
- Restrict the length of it to around 150-160 characters.
- Including your main keywords is always helpful.
- Think of what the searcher wants to know, and pitch your point across concisely.
- All meta descriptions should be unique.
For WordPress CMS users, you can edit your meta description if you install a plugin like WordPress SEO by Yoast. After installing and activating the plugin, you should be able to see this option below where you normally write your posts. Simple!